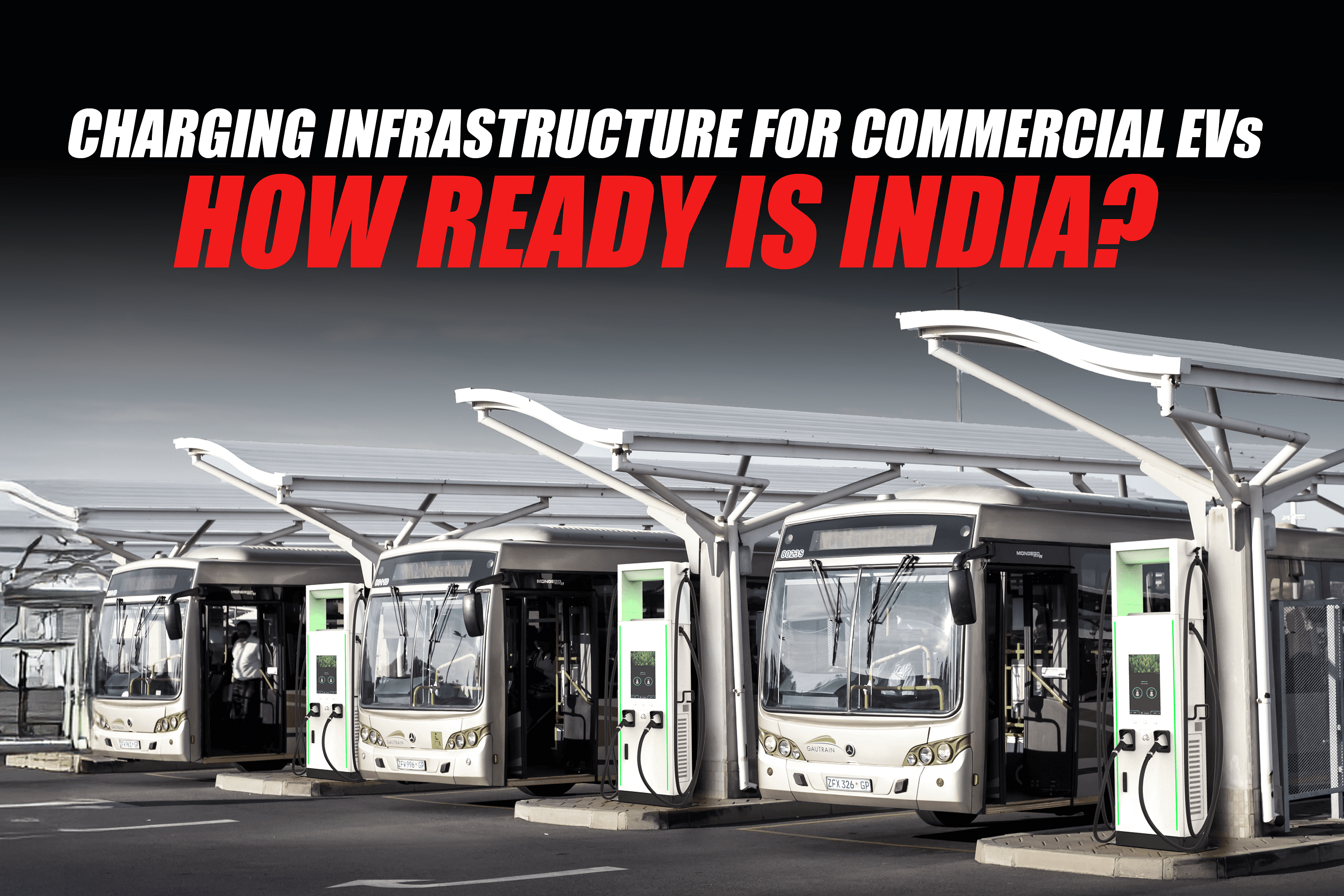
India is moving rapidly towards cleaner mobility. Companies, policymakers, and manufacturers are all set in one direction, electrifying mobility, and that too in the commercial vehicle segment. But with changing vehicle models and fleet size growth, the question in earnest remains: Is the charging facility for electric commercial vehicles ready to handle the demand?
Let us gauge India's readiness, step by step.
India's Commercial EV Drive: Firm Intent, Actual Shortfalls
India has been advancing with the adoption of electric vehicles, the majority of states today provide incentives for purchasing them. The central government supports EV adoption with initiatives such as FAME II. Startups and incumbent manufacturers are introducing electric commercial vehicles (ECVs) across the board, from three-wheelers to heavy trucks.
But something is certain. Vehicles are on the rise. Charging stations are not quick enough, in the proper locations, and with the necessary power levels. The demand-supply gap is increasing, particularly for the commercial segment.
Why Commercial EV Charging is Different
Commercial vehicle needs are different from passenger vehicles. Private EV owners charge their vehicles at night. Commercial EVs operate throughout the day, some transport goods and others move people.
What then does an electric commercial vehicle require?
- Fast chargers (50 kW and above) at regular intervals
- Depot charging stations for fleets
- Battery swapping for three-wheelers and light vehicles
- Grid support where vehicles drive, not only in big cities
In essence, commercial charging infrastructure needs to keep up with the tempo and rhythm of business activity.
Existing Infrastructure: A Mixed Picture
India has added about 12,000 public charging points until mid-2025, but the figure is misleading. A majority are for private EVs, only a handful provide support for heavy vehicles or large fleets.
- DC fast chargers are scarce. Even fewer are available for public commercial use.
- Battery swapping is expanding but restricted to urban centers and particular vehicles.
- Depot chargers can be found primarily in government or corporate agreements.
So, infrastructure does exist, but it is not always available to commercial users where and when they require it.
Main Challenges Hindering Growth
1. High Costs
Installing a commercial EV charging station is costly. The hardware price is high. Land is limited. Power upgrades are additional expenses. Small fleet owners cannot afford to make this investment.
2. Grid Limitations
Fast chargers consume heavy power. Weak grids cannot support heavy usage. The best stations will experience outages or delays without grid upgrades.
3. Regulatory Gaps
EV policies are different in each state. Land leases are favored in some. Others have high electricity prices. Private investment lags without clear, consistent rules.
4. Location Trouble
Cities run out of room. Warehouses and logistics parks are on the outskirts of cities. Pricing there requires planning and permits. Most such projects stall or are abandoned.
Recent Efforts Showing Promise
Despite this, progress is being made. Government and private players alike are moving ahead.
- Tata Power, BPCL, and IOCL are building multi-point charging hubs.
- Delhi’s EV Policy 2.0 targets commercial fleets and supports infrastructure.
- NTPC and REIL are rolling out fast chargers on highways.
- Flipkart, Amazon, and Zomato are building in-house charging yards.
These are important moves, but for impact scale is key. Isolated success won't meet national demand.
What India Needs to Do Next
1. Plan Charging Around Movement
Charging points have to keep pace with vehicle movement. Place them close to warehouses, highways, delivery hubs, and bus stations. Don't limit them to the heart of cities.
2. Develop Uniform Policy
The center needs to release a uniform template. States can modify it but have to abide by core guidelines, on power tariffs, land usage, and permissions.
3. Supplement with Smart Grids
Smart grids will be able to regulate load more efficiently. Employ solar panels, battery banks, and real-time data to ensure power keeps coming.
4. Provide Financial Incentives
Support needs to go beyond customers. Manufacturers of commercial charging facilities require subsidies, tax relief, and low-interest loans.
The Road Ahead: Ready, But Not Fully Equipped
India has a vision, the market is primed, and electric commercial vehicles are invading every segment. But the success of this transition hinges on one thing, electric fleet charging infrastructure.
Unless it has robust infrastructure, adoption will stop, fleets will not scale, business models will collapse, and emissions will not fall. But with the correct measures, planning, incentives, and policy, India can catch up.
For more articles and news, stay updated with 91trucks. Subscribe to our YouTube channel and follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn for the latest videos and updates from the automotive world!
Read More:
Web Stories
Latest Three Wheelers News
Categories
91trucks is a rapidly growing digital platform that offers the latest updates and comprehensive information about the commercial vehicle industry.